The history of trigonometry is inextricably linked with astronomy, because it was to solve the problems of this science that the ancient scientists began to study the ratios of various quantities in a triangle.
Today, trigonometry ismicrosection of mathematics, studying the relationship between the values of the angles and lengths of the sides of triangles, as well as engaged in the analysis of algebraic identities of trigonometric functions.
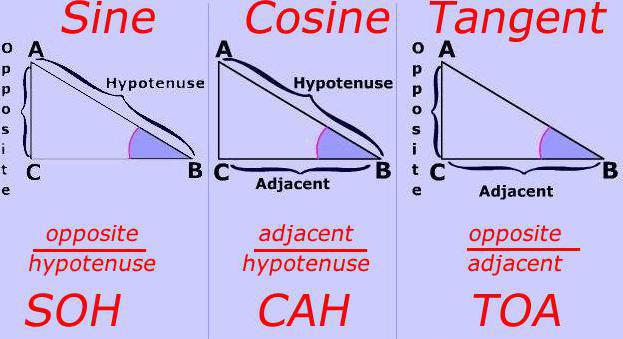
The term "trigonometry"
The term itself, which gave the name to this sectionmathematics was first discovered in the title of a book by the German scientist and mathematician Pitiskus in 1505. The word "trigonometry" has a Greek origin and means "measuring a triangle." To be more precise, we are not talking about the literal dimension of this figure, but about its solution, that is, the determination of the values of its unknown elements using known ones.
Trigonometry Overview
The history of trigonometry began more than twothousands of years ago. Initially, its occurrence was associated with the need to clarify the ratios of the angles and sides of the triangle. In the process of research it turned out that the mathematical expression of these relations requires the introduction of special trigonometric functions, which were originally designed as numerical tables.
For many science related mathsdevelopment has become precisely the history of trigonometry. The origin of the units of measurement of angles (degrees), associated with the research of scientists of ancient Babylon, is based on the hexagonal system of calculus, which gave rise to modern decimal, used in many applied sciences.
It is assumed that initially trigonometryexisted as part of astronomy. Then she began to be used in architecture. And over time, the expediency of applying this science in various fields of human activity. This, in particular, astronomy, sea and air navigation, acoustics, optics, electronics, architecture and others.
Early Age Trigonometry
Guided by the data on the remaining scientificrelics, the researchers concluded that the history of trigonometry is related to the work of the Greek astronomer Hipparchus, who first thought about finding ways to solve triangles (spherical). His writings date back to the 2nd century BC.

The history of the development of trigonometry in ancient Greece is connected with the name of the astronomer Ptolemy - the author of the geocentric system of the world, which prevailed before Copernicus.
Greek astronomers were not aware of sinuses,cosines and tangents. They used tables that allow them to find the value of the chord of a circle using a constricted arc. The units for measuring the chord were degrees, minutes, and seconds. One degree equated to the sixtieth of the radius.
Also the studies of the ancient Greeks advanceddevelopment of spherical trigonometry. In particular, Euclid in his "Principles" gives a theorem on the regularities of the ratios of the volumes of balls of different diameters. His works in this area became a kind of impetus for the development of related fields of knowledge. This, in particular, the technology of astronomical instruments, the theory of cartographic projections, the system of celestial coordinates, etc.

Middle Ages: research by Indian scientists
Considerable success was achieved by Indian medieval astronomers. The death of ancient science in the IV century led to the relocation of the center of development of mathematics to India.
The history of trigonometry asA separate section of mathematical doctrine began in the Middle Ages. It was then that scientists replaced the chords with sinuses. This discovery made it possible to introduce functions relating to the study of the sides and angles of a right triangle. That is precisely when trigonometry began to isolate itself from astronomy, turning into a branch of mathematics.
The first tables of sines were at Aryabhata, they were held in 3about, 4about, 5about. Later, detailed versions of the tables appeared: in particular, Bhaskara brought a table of sines through 1about.

The history of the development of trigonometry in Europe
After translating Arabic treatises into Latin(XII-XIII c) most of the ideas of Indian and Persian scientists were borrowed by European science. The first mentions of trigonometry in Europe refer to the 12th century.
According to researchers, the history of trigonometry inEurope is associated with the name of the Englishman Richard Wallingford, who was the author of the work "Four treatises on direct and converting chords. It was his work was the first work, which is entirely devoted to trigonometry. By the XV century, many authors in their writings mention trigonometric functions.
The history of trigonometry: New time
In modern times, most scientists began to realizeThe extreme importance of trigonometry, not only in astronomy and astrology, but also in other areas of life. This is, first of all, artillery, optics and navigation in distant sea voyages. Therefore, in the second half of the XVI century, this topic interested many prominent people of that time, including Nicolaus Copernicus, Johann Kepler, Francois Wieta. Copernicus led trigonometry several chapters of his treatise On the Rotation of the Celestial Spheres (1543). A little later, in the 60s of the XVI century, Retik - a student of Copernicus - in his work “The Optical Part of Astronomy” gives fifteen-digit trigonometric tables.

Merit Leonard Euler
Giving trigonometry modern content andThe view has become a merit of Leonard Euler. His treatise "Introduction to the Analysis of the Infinite" (1748) contains the definition of the term "trigonometric functions", which is equivalent to the modern. Thus, this scientist was able to determine the inverse function. But that's not all.
Определение тригонометрических функций на всей the numerical line was made possible by Euler's studies of not only permissible negative angles, but also more than 360 ° angles. It was he who in his works for the first time proved that the cosine and the tangent of a right angle are negative. Decomposition of whole powers of cosine and sine has also become a merit of this scientist. The general theory of trigonometric series and the study of the convergence of the series obtained were not the objects of Euler's research. However, working on the solution of related problems, he made many discoveries in this area. It was thanks to his work that the history of trigonometry continued. Briefly in his writings, he touched on issues of spherical trigonometry.

Trigonometry applications
Trigonometry does not apply to applied sciences, inin real daily life, her tasks are rarely applied. However, this fact does not diminish its significance. For example, the triangulation technique is very important, which allows astronomers to accurately measure the distance to nearby stars and control the satellite navigation systems.
Также тригонометрию применяют в навигации, теории music, acoustics, optics, analysis of financial markets, electronics, probability theory, statistics, biology, medicine (for example, in decoding ultrasound studies of ultrasound and computed tomography), pharmaceuticals, chemistry, number theory, seismology, meteorology, oceanology, cartography, many sections physics, topography and geodesy, architecture, phonetics, economics, electronic engineering, mechanical engineering, computer graphics, crystallography, etc. The history of trigonometry and its role in the study of natural and mathematical sciences are studied and to this day. Perhaps in the future there will be even more areas of its application.
The history of the origin of basic concepts
The history of the emergence and development of trigonometry has more than one century. The introduction of the concepts that form the basis of this branch of mathematical science was also not simultaneous.

The word "cosine" appeared much later. This term is an abbreviated version of the Latin phrase “extra sinus”.
The occurrence of tangents is associated with decodingproblems of determining the length of the shadow. The term “tangent” in the 10th century introduced the Arabic mathematician Abul-Wafa, who compiled the first tables for the definition of tangents and cotangents. But European scientists did not know about these achievements. The German mathematician and astronomer Regimontan rediscovers these concepts in 1467. The proof of the tangent theorem is his merit. And this term is translated as "relating."







