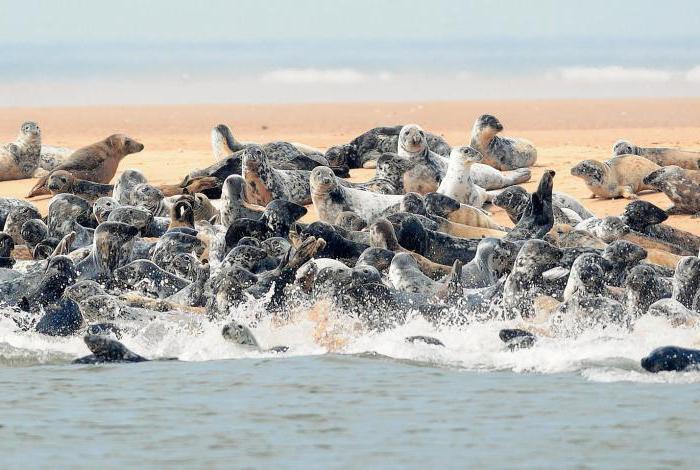
Find out where all life came from on earth -The task is complex, over which mankind has been fighting for a long time. There are quite a few hypotheses, from the theological (divine) to the fantastic (the theory of the creation of the world by alien beings). In this case, one of the most popular until now was proposed in the 19 century by Charles Darwin. Its essence lies in the fact that all kinds of life on Earth (including humans) appeared during the evolution, gradually taking its present shape. Someone agrees with this hypothesis, some do not, however, its significance for the whole of science as a whole is undeniable.
The main provisions of the evolutionary theory of Darwinthe following. All living species on the planet have never been created. Organic forms that arose naturally, gradually changed in accordance with the conditions surrounding them. This transformation is based on heredity, variability and natural selection. The last Darwin was named as a struggle for existence. As a result of evolution, a variety of different species appeared in nature, while they are all maximally adapted in the environment in which they are located.
The main provisions of Darwin's theory are described in hisa book published in 1859. Here the scientist clearly demonstrated how minor changes in individual organisms lead to the transformation of domestic animals and agricultural plants. As a result, a person chooses the species that are most valuable for him, and receives from them offspring. A similar process, the scientist believes, occurs in nature. In his book Darwin describes the origin of species as a long natural process, however, absolutely nonrandom.
So, the variability can be of two types:definite and indefinite. The first arises as a result of the influence of external factors on the body, and, as a rule, if they disappear, then the next generation these features no longer manifest. Uncertain variability is inherited regardless of environmental conditions. It is this that is the driving factor in the development of species.
The main provisions of Darwin's theory are based onThe fact that the material of evolution is hereditary variability. It leads to the fact that the individual has successful or unsuccessful properties as a result of crossing it with a close appearance. Modern biology has introduced the name "mutations".
In the struggle for existence, those organisms thathave less adaptability to environmental conditions, or die, or begin to multiply less. The closer in structure to the individuals on the same territory, the greater the competition between them, resulting in many of them dying. In life there are basically those who acquire different properties (they use a variety of food, remedies, attacks, etc.). As a result of divergence (divergence of characteristics), splitting of one species into varieties can occur, which in the end can become an independent unit.
The main theses of Darwin's theory suggest that,that dwelling in stable conditions leads to a slowdown in evolution. That is, it is global climate change that can lead to the emergence of a new species that is significantly different from its ancestors. The scientist gives a lot of evidence to the fact that it is natural selection that determines the fitness of organisms to the changing environmental conditions. For example, in animals it is coloring, in some plants and trees - the ability to reproduce by dispersing seeds and fruits, etc.
It should be noted that the main theses of the theoryDarwin are important enough for the further development of science. His works are still being studied, and a large number of studies and experiments are carried out on them.