Russia is the largest country in the world. What territory does it occupy? What are the main features of the geopolitical and economic-geographical position of Russia?
Basic information about Russia
The modern state of Russia appeared on the world map only in 1991. Although the beginnings of its statehood arose much earlier - about eleven centuries ago.
Modern Russia is a republic of federativetype It consists of 85 subjects, different in size and population. Russia is a multinational state in which representatives of more than two hundred ethnic groups live.
The country is the world's largest exporteroil, gas, diamonds, platinum and titanium. It is also one of the world leaders in the production of ammonia, mineral fertilizers and weapons. The Russian Federation is one of the leading space and nuclear powers of the planet.

What are the main features of the geographical position of Russia? This will be discussed further.
Geographical position of Russia: territory, area, extreme points and population
The country occupies a huge area of 17.1 million square meters.km (first place in the world in terms of size). It stretches for ten thousand kilometers, from the shores of the Black and Baltic Seas in the west to the Bering Strait in the east. The length of the country from north to east is 4000 km.
The extreme points of the territory of Russia are as follows (all of them are displayed with red conventional icons on the map below):
- northern - Cape Fleegeli (within the limits of Franz Josef Land);
- southern - near the mountains Kichensuv (in Dagestan);
- Western - on the Baltic Spit (in the Kaliningrad region);
- eastern - Ratmanov Island (in the Bering Strait).
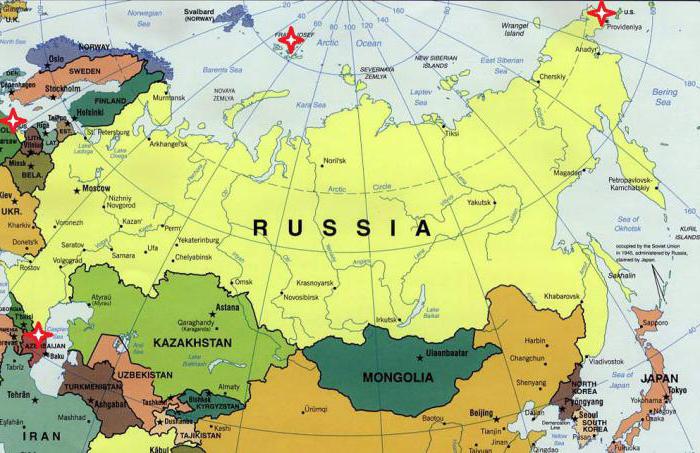
Russia directly borders with 14 independentStates, as well as with two partially recognized countries (Abkhazia and South Ossetia). A curious fact: about 75% of the country's territory is located in Asia, but in its European part almost 80% of Russians live. The total population of Russia: about 147 million people (as of January 1, 2017).
Geographical position of Russia
The whole territory of Russia is located withinThe northern hemisphere of the Earth and almost all (with the exception of a small part of the Chukotka Autonomous Region) - within the Eastern Hemisphere. The state is located in the northern and central part of Eurasia and occupies almost 30% of Asia.

From the north of the coast of Russia washed the North SeaArctic Ocean, and in the east - the Pacific. In the western part, it has access to the Black Sea, which belongs to the Atlantic Ocean basin. The country has the longest coastline among all countries of the world - more than 37 thousand kilometers. These are the main features of the physical and geographical position of Russia.
The country has a tremendous wealth anddiversity of natural resource potential. In its open spaces there are the richest deposits of oil and gas, iron ore, titanium, tin, nickel, copper, uranium, gold and diamonds. Russia also has enormous water and forest resources. In particular, about 45% of its area is covered with forest.

Стоит выделить и другие важные особенности Physical and geographical position of Russia. So, most of the country is located north of the 60th degree of northern latitude, in the permafrost zone. And in these difficult climatic conditions, millions of people are forced to live. All this, of course, left its mark on the life, culture and traditions of the Russian people.
Russia is in the area of the so-calledrisky farming. This means that the development of agriculture in the majority of it is difficult or impossible. So, if in the northern regions of the country there is not enough heat, in the south, on the contrary, there is a shortage of moisture. These features of the geographical position of Russia have a significant impact on the agro-industrial sector of its economy, which is in dire need of government subsidies.
Components and levels of economic and geographical position of the country
Under the economic and geographical position (EGP)a country or region understands the totality of relations and relations of individual enterprises, settlements and districts with objects that are located outside the country and have a strong influence on it.
Scientists distinguish the following components of EGP:
- transport;
- industrial;
- agrogeographical;
- demographic;
- recreational;
- market (position relative to markets).
The EGP of a country or region is evaluated at three different levels: at the micro, meso, and macro levels. Next, we will assess Russia's macro position in relation to the world as a whole.
Features, changes in the economic and geographical position of Russia
Размер территории – важнейшая особенность и benefit of the economic and geographical position of the Russian Federation, with which many prospects are connected. It allows the country to ensure a competent division of labor, rationally deploy its productive forces, etc. Russia borders on fourteen countries of Eurasia, among which are powerful raw materials bases in China, Ukraine, and Kazakhstan. Numerous transport corridors provide close cooperation with the states of Western and Central Europe.
Here, perhaps, are the main features of Russia's geographic location of an economic nature. How has it changed in recent decades? And did it change?
After the collapse of the USSR, the economic and geographicalThe situation of the country has noticeably deteriorated. And above all, transport. After all, Russia's access to the strategically important waters of the Black and Baltic Seas in the early 1990s was significantly limited, and the country itself was a few hundred kilometers away from the highly developed European countries. In addition, Russia has lost a lot of traditional markets.
The geopolitical position of Russia
The geopolitical position is the place of the country onworld political arena, its relationship with other states. On the whole, Russia has ample opportunities for economic, political, military, scientific and cultural cooperation with many countries of Eurasia and the planet.
However, not with all states this relationshipstack up in the best way. Thus, in recent years, Russia's relations with a number of NATO countries — the Czech Republic, Romania, and Poland — which were once close allies of the Soviet Union — have significantly deteriorated. This fact, by the way, is called the largest geopolitical defeat of the Russian Federation in the new century.

Difficult and rather tense remainRussia's relations with a number of post-Soviet states: Ukraine, Georgia, Moldova, the countries of the Baltic region. The geopolitical position of the country significantly changed in 2014 with the annexation of the Crimean Peninsula (in particular, in the Black Sea region).
Changes in the geopolitical position of Russia in the twentieth century
If we consider the twentieth century, the most tangiblethe rearrangement of forces in the European and world political arena occurred in 1991. The collapse of the powerful power of the USSR led to a number of fundamental changes in the geopolitical position of Russia:
- along the perimeter of Russia, more than a dozen young and independent states emerged, with which it was necessary to establish a new type of relations;
- the Soviet military presence was finally liquidated in several countries of Eastern and Central Europe;
- Russia received a rather problematic and vulnerable enclave - Kaliningrad region;
- The NATO military bloc gradually approached directly to the borders of the Russian Federation.

At the same time, over the past decades, quite strong and mutually beneficial relations of Russia with Germany, China, Japan, and India have been established.
As a conclusion: Russia in the modern world
Russia occupies a vast territory, possessingtremendous human and natural resource potential. Today it is the largest state in the world and an important player in the global arena. We can single out the most important features of the geographical position of Russia, here they are:
- The vastness of the occupied space and the enormous length of the borders.
- Awesome variety of natural conditions and resources.
- Mosaic (uneven) settlement and economic development of the territory.
- Extensive trade, military and political cooperation with various neighboring countries, including the leading economies of the modern world.
- The volatility and instability of the geopolitical position of the country over the past decades.
Features of the geographical position of Russiadifferent extreme profitability. But these benefits (natural, economic, strategic and geopolitical) are important to learn how to use correctly and rationally, directing them to increase the power of the country and the well-being of its citizens.