Organic chemistry is a very complex science, butinteresting. After all, the compounds of the same elements, in different quantities and sequences, promote the formation of substances with different properties. Let's look at compounds of the carbonyl group called "ketones" (chemical properties, physical features, methods of their synthesis). And also we compare them with other substances of the same kind - aldehydes.
Ketones
This word is a common name for a whole class of substances of organic nature, in molecules of which the carbonyl group (C = O) is associated with two carbon radicals.
Ketones are similar in structure to aldehydes and carboxylic acids. However, they simultaneously contain two C atoms (carbon or carbon) connected to C = O.

Formula
The general formula for this class of substances is as follows: R1-CO-R2.
To make it more understandable, as a rule, it is recorded as follows.

In it, C = O is a carbonyl group. A r1 and R2 - these are carbon radicals. There may be various compounds in their place, but carbon must necessarily be in their composition.
Aldehydes and ketones
The physical and chemical properties of these groups of substances are quite similar to each other. For this reason, they are often considered together.
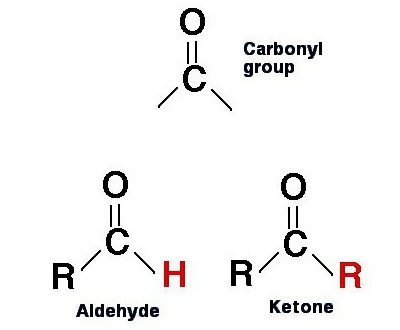
The fact is that aldehydes also contain in theirmolecules carbonyl group. They even have very similar formulas with ketones. However, if in the substances under consideration C = O is attached to 2 radicals, then in aldehydes it is only one, instead of the second, it is a hydrogen atom: R-CO-H.
As an example, one can cite the formula of a substance of this class — formaldehyde, better known to all as formalin.

Based on the formula CH2O, it is clear that its carbonyl group is connected not with one, but with two atoms N.
Physical properties
Before you deal with the chemical properties of aldehydes and ketones, it is worth considering their physical features.

- Ketones are low melting solids or volatile liquids. Lower class representatives dissolve perfectly in H2Oh, and interact well with organic solvents.
Individual representatives (for example, CH3SOSN3) remarkably soluble in water, and absolutely in any proportions.
Unlike alcohols and carboxylic acids, ketoneshave greater volatility, with the same molecular weight. This is due to the inability of these compounds to create bonds with H, as H-CO-R can. - Different types of aldehydes can exist in various aggregative states. So the higher R-CO-H are insoluble solids. The lower ones are liquids, some of which mix well with H2Oh, but some of them are only soluble in water, but no more.
The simplest substance of this type - ant aldehyde - is a gas, which is characterized by a sharp smell. This substance is perfectly soluble in H2ABOUT.
Most famous ketones
There are many substances R1-CO-R2however, there are not so many famous ones. The first is dimethyl ketone, which we all know as acetone.
Among other ketones, whose chemical propertiesacetophenone (methylphenyl ketone) is actively used in industry. Unlike acetone and butanone, its smell is quite pleasant, which is why it is used in perfumery.
For example, cyclohexanone refers to the typical representatives of R1-CO-R2, and is most often used in the production of solvents.
Not to mention the diketones. This name is R1-CO-R2which have not one but two carbonyl groups in the composition. Thus, their formula looks like: R1-CO-CO-R2. One of the most simple, but widely used in the food industry, representatives of diketones is diacetyl (2,3-butanedione).
The listed substances are only small.a list of ketones synthesized by scientists (chemical properties are discussed below). In fact, there are more of them, but not everyone has found an application. Moreover, it is worth considering that many of them are toxic.
Chemical properties of ketones
Substances in this category are capable of reacting with various substances. This is their particular chemical properties.
- Ketones are capable of attaching H to themselves (reactionhydrogenation). However, to produce this reaction, the presence of catalysts in the form of nickel, cobalt, cuprum, platinum, palladium and other metal atoms is necessary. As a result of the reaction R1-CO-R2 evolve to secondary alcohols.
Also, when interacting with hydrogen in the presence of alkali metals or Mg amalgam, glycols are obtained from ketones. - Ketones with at least onealpha-hydrogenic atoms, as a rule, are affected by the tautomerization of keto-enol. It is catalyzed not only with acids, but also with bases. Usually keto-form is a more stable phenomenon than enol. This equilibrium makes it possible to synthesize ketones by hydration of alkynes. The relative stabilization of the enol keto form by conjugation leads to a rather strong acidity R1-CO-R2 (if you compare them with alkanes).
- These substances may react with ammonia. However, they are very slow.
- Ketones interact with hydrocyanic acid. As a result, α-oxynitriles arise, the saponification of which promotes the appearance of α-hydroxy acids.
- Reacting with alkyl magnesium halides leads to the formation of secondary alcohols.
- Joining NaHSO3 contributes to the emergence of hydrosulfite (bisulfite) derivatives. It is worth remembering that only methyl ketones are capable of reacting in the fat series.
In addition to ketones, aldehydes can likewise interact with sodium hydrosulfite.
When heated with a solution of NaHCO3 (baking soda) or mineral acid, derived from NaHSO3 may decompose, accompanied by the release of free ketone. - In the course of the reaction R1-CO-R2 with NH2OH (hydroxylamine) are formed ketoximes and as a by-product - H2ABOUT.
- In reactions involving hydrazine, hydrazones are formed (the ratio of the taken substances is 1: 1) or azines (1: 2).
If the product (hydrazone) obtained from the reaction under the action of temperature reacts with caustic potassium, N and saturated hydrocarbons will be released. This process is referred to as the Kizhner reaction. - As mentioned above, aldehydes and ketones have similar chemical properties and production process. At the same time acetals R1-CO-R2 more complex than acetals R-CO-H are formed. They appear as a result of the action of the orthoformonic and orthosilicon acids on ketones.
- In conditions with a higher concentration of alkalis (for example, when heated with concentrated H₂SO₄) R1-CO-R2 undergo intermolecular dehydration with the formation of unsaturated ketones.
- If in reaction with R1-CO-R2 alkalis are present, ketones undergo aldol condensation. As a result, β-ketospirits are formed that can easily lose the H molecule.2ABOUT.
- The chemical properties of ketones are exemplary in the example of acetone that has reacted with mesityl oxide. In this case, a new substance called "phoron" is formed.
- The chemical properties of the organic matter under consideration include the Leukart-Wallach reaction, which contributes to the reduction of ketones.
What is R1-CO-R2 derived from
After reviewing the properties of the substances under consideration, it is worth finding out the most common methods of their synthesis.
- One of the most well-known reactions for the production of ketones is the alkylation and acylation of aromatic compounds in the presence of acid catalysts (AlCl3FeCI3, mineral acids, oxides, cation exchange resins, etc.). This method is known as the Friedel-Crafts reaction.
- Ketones are synthesized by hydrolysis of ketimine and vice-diols. In the case of the latter, the presence of mineral acids as catalysts is necessary.
- Also, to obtain ketones, the hydration of acetylene homologs is used or, as it is called, the Kucherov reaction.
- Reactions Guben-Gesh.
- Cyclization Ruzicki suitable for the synthesis of cycloketones.
- Also, these substances are extracted from tertiary peroxoesters by rearranging Kriege.
- There are several ways to synthesize ketones inreaction time of oxidation of secondary alcohols. Depending on the active compound, 4 reactions are distinguished: Swerna, Kornblum, Corey-Kim and Parik-Dering.
Scope of application
Having dealt with the chemical properties and the production of ketones, it is worth knowing where these substances are used.

As mentioned above, most of them are used in the chemical industry as solvents for varnishes and enamels, as well as in the production of polymers.
Besides this, some R1-CO-R2 not bad proved as fragrances. As such, ketones (benzophenone, acetophenone, and others) are used in perfumery and cooking.
Also, acetophenone is used as a component for the manufacture of sleeping pills.

Benzophenone, due to its ability to absorb harmful radiation, is a frequent ingredient of anti-tan cosmetics and at the same time a preservative.
Effects of R1-CO-R2 on the body
Learning what compounds are called ketones(chemical properties, application, synthesis and other data about them), it is worth getting acquainted with the biological characteristics of these substances. In other words, find out how they act on living organisms.
Despite the rather frequent use of R1-CO-R2 in industry, you should always remember that such compounds are very toxic. Many of them are carcinogenic and mutagenic.
Special representatives can cause irritation on the mucous membranes, up to burns. Alicyclic R1-CO-R2 can affect the body like drugs.
However, not all substances of this kind are harmful. The fact is that some of them are actively involved in the metabolism of biological organisms.
Also, ketones are unique markers of impaired carbon metabolism and insulin deficiency. In the analysis of urine and blood, the presence of R1-CO-R2 evidence of various metabolic disorders, including hyperglycemia and ketoacidosis.



