Weak interaction is one of fourfundamental forces governing all matter in the universe. The other three are gravity, electromagnetism and strong interaction. While other forces hold things together, weak force plays a big role in their destruction.
Weak interaction is stronger than gravity, but iteffective only at very short distances. The force acts at the subatomic level and plays a crucial role in providing stars with energy and creating elements. It is also responsible for most of the natural radiation in the universe.
Fermi theory
Итальянский физик Энрико Ферми в 1933 г.developed a theory to explain beta decay — the process of converting a neutron into a proton and displacing an electron, which is often called a beta particle in this context. He identified a new type of force, the so-called weak interaction, which was responsible for the decay, the fundamental process of converting a neutron into a proton, a neutrino and an electron, which was later defined as an antineutrino.
Fermi originally supposed that took placezero distance and grip. Two particles had to be in contact for the force to work. Since then, it turned out that the weak interaction is actually a force of attraction, which manifests itself at an extremely short distance equal to 0.1% of the diameter of the proton.

Electroweak force
In radioactive decays, weak forceabout 100,000 times smaller than electromagnetic. However, it is currently known that it is internally equal to electromagnetic, and these two distinctly different phenomena are believed to be manifestations of a single electro-weak force. This is confirmed by the fact that they are combined at energies of more than 100 GeV.
It is sometimes said that weak interaction manifests itself in the breakdown of molecules. However, intermolecular forces are of an electrostatic nature. They were discovered by van der Waals and bear his name.

Standard model
Weak interaction in physics is part ofstandard model - the theory of elementary particles, which describes the fundamental structure of matter, using a set of elegant equations. According to this model, elementary particles, i.e., that which cannot be divided into smaller parts, are the building blocks of the Universe.
One of these particles is the quark. Scientists do not assume the existence of something smaller, but they are still looking for. There are 6 types, or varieties of quarks. Place them in ascending mass order:
- upper;
- lower;
- strange;
- charmed;
- charming;
- true.
In various combinations, they form manyvarious types of subatomic particles. For example, protons and neutrons - large particles of the atomic nucleus - are made up of three quarks each. The top two and bottom make up a proton. The upper and lower two form a neutron. Changing a quark grade can change a proton into a neutron, thereby turning one element into another.
Another type of elementary particle is the boson.These particles are carriers of interaction, which consist of beams of energy. Photons are one type of boson, gluons are different. Each of these four forces is the result of a vector exchange of interactions. Strong interaction is carried out by a gluon, and electromagnetic - by a photon. Graviton is theoretically a carrier of gravity, but it was not found.

W- and Z-bosons
The weak interaction is carried by the W and Z bosons.These particles were predicted by Nobel Prize laureates Stephen Weinberg, Sheldon Salam and Abdus Gleshow in the 60s of the last century, and they were discovered in 1983 at the European Nuclear Research Organization CERN.
W-bosons are electrically charged and are designated by the symbols W+ (positively charged) and W- (negatively charged).W-boson changes the composition of particles. By emitting an electrically charged W-boson, a weak force changes the quark grade, turning a proton into a neutron or vice versa. That is what causes nuclear fusion and makes the stars burn.
This reaction creates heavier elements.which, ultimately, are thrown into space by supernova explosions to become the building blocks for planets, plants, people and everything else on Earth.

Neutral current
The z-boson is neutral and carries a weak neutral current.Its interaction with particles is difficult to detect. Experimental searches for the W and Z bosons in the 1960s led scientists to a theory combining electromagnetic and weak forces into a single “electro-weak”. However, the theory required carrier particles to be weightless, and scientists knew that, theoretically, the W-boson should be heavy to explain its short range. Theorists attributed the mass W to the invisible mechanism, called the Higgs mechanism, which provides for the existence of the Higgs boson.
In 2012, CERN reported that scientists, using the world's largest accelerator - the Large Hadron Collider - observed a new particle “corresponding to the Higgs boson”.
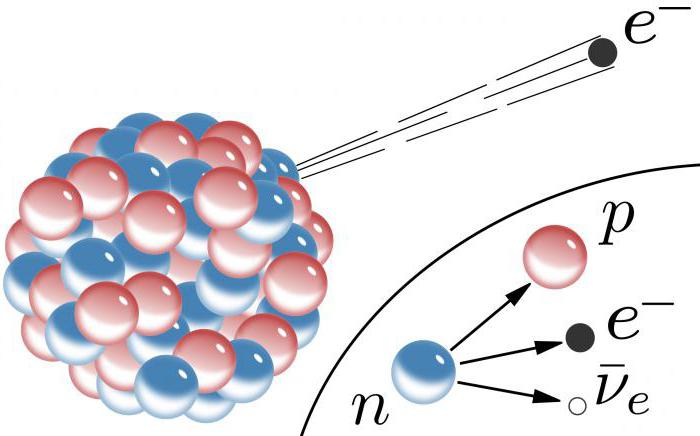
Beta decay
Weak interaction occurs at β-decay -process in which the proton turns into a neutron and vice versa. It occurs when in a nucleus with too many neutrons or protons one of them is converted into another.
Beta decay can be done in one of two ways:
- With minus beta decay, sometimes written as β- decay, the neutron is split into a proton, antineutrino and electron.
- Weak interaction manifests itself in the decay of atomic nuclei, sometimes written as β+decay when a proton splits into a neutron, neutrino, and positron.
One element can turn into another,when one of its neutrons spontaneously turns into a proton through minus-beta decay, or when one of its protons spontaneously turns into a neutron through β+-decay.
Dual beta decay occurs when at core 2protons are simultaneously transformed into 2 neutrons or vice versa, as a result of which 2 electron-antineutrinos and 2 beta particles are emitted. In a hypothetical neutrinoless double beta decay, neutrinos are not formed.

Electronic capture
Proton can turn into a neutron bya process called electron capture or K capture. When there is an excess amount of protons in the nucleus relative to the number of neutrons, the electron, as a rule, from the inner electron shell seems to fall into the nucleus. The electron orbitals are captured by the parent nucleus, the products of which are the daughter nucleus and the neutrino. The atomic number of the resulting daughter nucleus is reduced by 1, but the total number of protons and neutrons remains the same.
Thermonuclear reaction
Weak interaction takes part in nuclear fusion - a reaction that energizes the sun and thermonuclear (hydrogen) bombs.
The first step in the fusion of hydrogen is the collision of two protons with sufficient force to overcome the mutual repulsion experienced by them due to their electromagnetic interaction.
If both particles are located close to each other, a strong interaction can bind them. This creates an unstable form of helium (2He), which has a nucleus with two protons, in contrast to the stable form (4Not), which has two neutrons and two protons.
At the next stage weak interaction comes into play. Due to an overabundance of protons, one of them undergoes beta decay. After that, other reactions, including intermediate formation and fusion 3Not, ultimately, form a stable 4Not.








