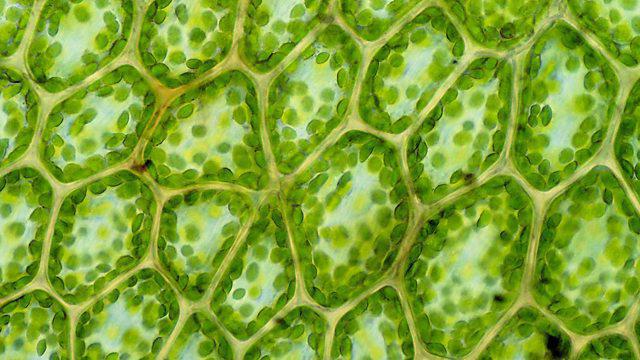
Органелла — это постоянное образование в клетке, which performs certain functions. They are also called organoids. Organella is what allows the cell to live. Just as an animal and a human being consist of organs, so every cell consists of organoids. They are diverse and perform all the functions that ensure the life of the cell: it is the metabolism, and their storage, and division.
What are the organelles?
Organella is a complex structure.Some of them may even have their own DNA and RNA. All cells contain mitochondria, ribosomes, lysosomes, cell center, Golgi apparatus (complex), endoplasmic reticulum (reticulum). Plants also have specific cellular organelles: vacuoles and plastids. Some also refer to organelles as microtubules and microfilaments.
Organella is a ribosome, vacuole, cell center, and many others. Let's take a closer look at the structure and functions of the organelles.
Mitochondria
These organelles provide the cell with energy - theyresponsible for cellular respiration. They are in plants, animals and fungi. These cellular organelles have two membranes: external and internal, between which there is an intermembrane space. What is inside the shells is called the matrix. It contains a variety of enzymes - substances necessary to accelerate chemical reactions. The inner membrane has folds - cristami. It is on them and the process of cellular respiration. In addition, mitochondrial DNA (mDNA) and mRNA, as well as ribosomes are located in the mitochondrial matrix, almost identical to those of prokaryotic cells.

Ribosome
This organoid is responsible for the translation process, withwhich is synthesized from individual amino acids protein. The structure of the ribosome organelle is simpler than mitochondria - it does not have membranes. This organoid consists of two parts (subunits) - small and large. When the ribosome is inactive, they are separated, and when it begins to synthesize protein, they are combined. Several ribosomes can also come together if the polypeptide chain they synthesize is very long. Such a structure is called a "polyribosome".

Lysosomes
The functions of the organelles of this species are reduced tothe implementation of cellular digestion. Lysosomes have one membrane, inside which are enzymes - catalysts for chemical reactions. Sometimes these organelles not only break down nutrients, but also digest whole organelles. This can happen during a long fasting of the cell and allows it to live for some time. Although if the nutrients still do not start flowing, the cell dies.

Cell center: structure and functions
This organella consists of two parts - centrioles.These formations are in the form of cylinders consisting of microtubules. The cell center is a very important organoid. He is involved in the formation of the spindle of division. In addition, it is the center of the microtubule organization.
Golgi Apparatus
Это комплекс дискообразных мембранных мешочков, called tanks. The functions of this organoid are to sort, store and transform certain substances. Mainly carbohydrates, which are part of glycocalyx, are synthesized here.

Structure and function of the endoplasmic reticulum
This is a network of tubes and pockets surrounded by onemembrane. There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum: smooth and rough. Ribosomes are located on the surface of the latter. Smooth and gritty reticulums perform various functions. The first is responsible for the synthesis of hormones, storage and conversion of carbohydrates. In addition, the rudiments of vacuoles, organoids characteristic of plant cells, are formed in it. The grungy endoplasmic reticulum contains on its surface ribosomes that produce a polypeptide chain of amino acids. Then it enters the endoplasmic reticulum, and a certain secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure of the protein is formed here (the chain is twisted in the right way).

Vacuoles
These are organelles of plant cells.They have one membrane. They accumulate cell sap. Vacuole is necessary to maintain turgor. She also participates in the osmosis process. In addition, there are contractile vacuoles. They are contained mainly in single-celled organisms living in water bodies, and serve as pumps that pump excess fluid from the cell.
Plastids: Varieties, Structure, and Functions
It is also a plant cell organelle.They are of three types: leukoplasts, chromoplasts and chloroplasts. The first are used to store spare nutrients, mainly starch. Chromoplasts contain various pigments. Thanks to them, the petals of plants are multi-colored. The body needs this first of all in order to attract pollinating insects.
Chloroplasts are the most important plastids.The largest number is in the leaves and stems of plants. They are responsible for photosynthesis - a chain of chemical reactions, in the process of which the organism gets organic from inorganic substances. These organelles have two membranes. The chloroplast matrix is called "stroma". It contains plastid DNA, RNA, enzymes, as well as starch inclusions. In chloroplasts are thylakoids - membrane formations in the form of a coin. Inside them, photosynthesis takes place. It also contains chlorophyll, which serves as a catalyst for chemical reactions. Chloroplast thylakoids are combined in piles - grana. Also in the organoids there are lamellae, which interconnect individual thylakoids and provide a link between them.
Movement organelles
They are mainly characteristic of single-celledorganisms. These include flagella and cilia. The first are present in Euglen, trypanosome, chlamydomonad. Flagella are also present in animal spermatozoa. Cilia have ciliates and other unicellular.
Microtubules
They provide transport of substances, as well as constant cell shape. Some scientists do not include microtubules as organelles.