In the economy, capital is the property of an individual or a legal entity, expressed in terms of money (sometimes in a commodity). There are several options for using this property:
- For private purposes.
- For preservation (purchase of antique goods or luxury objects).
- For augmentation.
Development of the term
Financial (money) capital is aresource economic life, which consists of financial (monetary documents and cash and non-cash funds) and real capital (resources invested in all kinds of economic activities). Economists treat the concept of "capital" in different ways.

Economists treat the concept of "capital" in different ways.Many of them believe that this concept is much broader than just "money." For example, Smith gives a characterization of capital as a certain stock of money supply and things. Ricardo goes further. He interprets capital as a material reserve of means for production. At the same time, he believes that it is extremely difficult to increase the price of capital. Economist Fischer interprets capital as the creation of services that form profit.
As a result, the financial structure of capital is a certain amount of benefits, expressed by mental, material and financial opportunities, which are used to increase the number of goods produced.
Capital in the theory of accounting, recognize all the funds invested in the assets of the organization or firm.
In the modern theory of economic termsfinancial capital is divided into real, expressed in highly intellectual form and material, and monetary (financial), expressed in cash and non-cash funds and securities.
Modern economists insist on another kind of capital - the human. It is formed due to the contribution to health and education of the workers that make up the labor resources of the enterprise.
Basic concept
Financial capital is cash and non-cashmeans that businessmen invest in business. Production has a demand not only for material capital. First of all, cash and non-cash funds temporarily not engaged in production go into business. They are necessary for obtaining capital goods.
Farms or organizations, not fully usingthe income received for current needs, save part of the funds. They go through financial markets to other farms or organizations that use them to purchase capital goods. Thus, there is an investment. The firm that applied the capital of the firm that retained it pays a loan interest. This percentage is the price of financial capital.
In economics, it is considered that financialmarkets have perfect competition. This means that neither savers nor firms that have received an investment have the ability to influence the interest rate by changing the amount of savings invested or changing the demand for them. Thus, the isostatic market interest rate is formed in the course of fair competition of both depositors and savers.

The demand for financial capital is the dependence oninterest payment for the investment. The fee is lower, the greater the amount of investment. The number of offers from firms-savers is also dependent on the interest rate: the higher it is, the higher the amount of savings.
Content of financial capital
Financial capital is recognized as cashdocuments and cash and non-cash funds. At the same time, valuable documents as a category are fully recognized as financial capital. Cash and non-cash funds can not be fully considered as such. Financial capital is not included in the money supply held by citizens of the country, in the cash desks of various enterprises and firms, as well as the key part of funds in settlement accounts with banks (as it goes to conduct sales transactions). Only a part of these funds, pledged in installments or in advance, can fall under the category of "financial capital of organizations". That part of the monetary resources of organizations that are applied as pension or insurance savings can also be a share of financial capital.
The diagram shows an approximate scheme of financial capital.
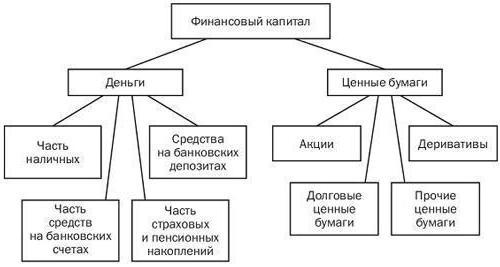
Economic background
Formation of the economic category "financialcapital "was provoked by the need for economic turnover. Considering the model of the circuit in the economy, one can see that organizations spend the share of their assets on settlement accounts in banks and in cash for costs of payment of economic resources and current expenses, and some in cash documents and deposits with banks for future spending. Households also accumulate savings and make various payments, including taxes. For these purposes, they also open accounts in banks, on deposits and have securities. The state, as a representative of the economic life, conducts payments for services, subsidies and goods, executes state money transfers and prints its securities. Funds, insurance and pension, participating in the economic cycle, reduce emerging risks in the course of social and economic activities, while keeping some of their active assets temporarily unoccupied.

Modern realities
In today's economic cyclefinancial capital is real capital. This is due to the fact that securities and money supply are transferred to tangible working capital and fixed assets.
Here it is necessary to take into account that financial capital does notall flows into the real. For example, some households in our country keep some of their active assets in foreign currency at home. Turnover in the economic sector of the share of real capital translates again into financial capital. This can happen, for example, due to a decrease in fixed capital due to deductions for depreciation, which fall on accounts in banks. In addition, financial capital is supplemented by constantly financial injections (the same purchase of securities). From this it follows that the financial capital works in parallel with the real capital.

Form of financial resources
As is clear from the foregoing, financial capital- this is the share of financial resources of the organization, which is in circulation and brings a certain income. That is, they are advanced and (or) invested resources, aimed at making a profit. The financial capital of an enterprise is the basis on which the organization is created and developed. It is the capital that characterizes the total value of enterprise funds in the non-material and material form and the investments in assets.
In the process of working capital is the guarantorinterests of the organization and the state. Therefore, it is the main object of financial management of the organization, and managers of the financial department are required to monitor the high efficiency of its use.
Signs of financial capital
Financial resources and capital are interrelated. Proceeding from this, several signs of the financial capital of the organization are singled out.

Affiliation
Here capital differs in its own andloan. By own capital, you can judge the total cost of the enterprise's funds (which are subject to the ownership rights of the enterprise). It includes reserve, additional, authorized capital and retained earnings.
Statutory, or stock capital - isThe minimum size of own property, which is a guarantee for creditors. Its size is stipulated in the charter of the organization (the minimum is set at the level of federal legislation).
Additional capital consists of a revaluation amountobjects of tangible property of the enterprise, the useful life of which is more than a year. Also in this capital are gratuitous values received by the firm, amounts earned in excess of the minimum value of placed securities and other monetary amounts falling under this category.
Reserve capital is the accumulation of profit from a deduction of profits for an unforeseen event: possible losses, repurchase of shares, etc. The amount of deductions is regulated by the articles of association.
Financial capital is the profit of an enterprise, which is practically the most basic part of it.
Borrowed capital - cash or other valuables that are raised on a returnable basis to improve the organization’s activities.
Investing
On the basis of investment distinguish circulating and fixed capital.
Part of the capital invested in fixed assets and non-current assets, and is fixed capital. Financial capital includes working capital.
All tangible and intangible assets,Organizations that are part of the financial capital are in constant circulation. On this basis, it is possible to divide it by the form of its location in the next round of turnover. It is a monetary form, productive and commodity.
Money form is an investment. Investments can be both in out-and current assets. In any case, they become productive.
At the production stage, capital changes into the form of a commodity (work, service).
The third and final stage - commodity capital is transformed into monetary capital through the sale of goods (services or works).
In parallel with these movements of capital, its value changes.
Financial Capital Management
This function usually lies with the management department.enterprises and means managing their own financial flows. To do this, the organization must have a long and short-term financial policy. Its main focus should be the attraction and proper distribution of financial flows.

Financial capital management is designed to solve several basic problems.
- Determination of the rationally required amount of equity capital.
- Attracting (if necessary) retained earnings or issuing shares to increase equity.
- Formulation and execution of dividend policy and structure of additional share issue.
The development of financial policy takes place in several stages.







