One of the most common children'sdiseases considered rickets. It is classified as a polyetiological disease of the metabolic type, caused by a lack of phosphorus and calcium salts in the body, as well as a violation of their transportation and metabolism. Rachitis is quite pronounced in children under one year old. Signs are expressed in violation of the development of the musculoskeletal system of the child. The lack of mineralization of osteoid (vitamin D deficiency) causes bone impairment.

Rickets in children under one year
The signs of the disease in the early period (2-3 months) are manifested by the following indicators:
- fearfulness and anxiety;
- anxious and shallow sleep;
- startling from harsh sounds;
- increased sweating of the face and occipital part of the head.
How is rickets in children
Up to a year, symptoms of rickets are divided by severity:
1. Easy degree. During this period, it is immediately noticeable how rachitis manifests itself in children:
- obvious compliance of the bones of the skull and the edges of the fontanel on the head;
- inability to hold the head;
- pronounced rib "beads".
2. The average degree. In 6-7 months become noticeable:
- muscle and nerve disorders;
- delayed motor skills (does not turn over and does not sit);
- slow growth and weight gain;
- there is a development of softening of the bones;
- broken teething schedule.
3. Severe. Manifested by various complications:

- damage to internal organs;
- abnormalities in the bone and nervous system;
- mental retardation and
physical development.
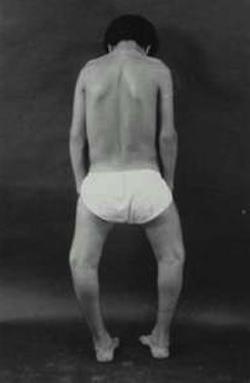
Closer to the year, it is already clearly visible what the rickets in children looks like:
- thickening of the ribs;
- slight protrusion or depression of the chest;
- poor posture and limb deformity.
Causes of the disease
Lack of vitamins related togroup B, vitamins A, zinc, magnesium and high-grade protein, is the most common reason for developing rickets in children under one year old. Signs of it are determined for many other reasons, for example, due to:
- genetic predisposition;
- lack of salts of phosphates and calcium;
- prematurity;
- improper feeding and frequent diseases;
- bad ecology;
- endocrine disorders.
The most common form of the disease is D-deficient rickets (with a lack of sunlight, vegetarianism, late introduction into the diet of animal products - meat, fish, yolk).
Of great importance is the prevention of the disease.
Preventive measures

The health of the child depends entirely on the behavior of the future mother, attentive attitude. Prevention should begin in the perinatal period:
- from walks in the fresh air;
- with good nutrition;
- with timely treatment of anemia and toxemia;
- from taking prescribed medications and vitamins.
Breastfeeding infants up to the year - the bestprevention of rickets. No artificial feeding will replace breast milk lactose, which significantly contributes to the absorption of calcium. Frequent walks in the fresh air are recommended. Allow the child to move actively.
It is undesirable for a child to consume flour products, as they inhibit the process of bone mineralization and absorption of calcium by the body.