Dissemination is the spread of a pathogen.infection or tumor cells from the primary focus of the disease throughout the organ or body. This is done through the bloodstream and lymphatic system. After dissemination, a process of generalization usually takes place, representing the development of a multitude of foci. Such secondary manifestations are called metastases.

Types of disease foci and their characteristics
The presence of foci in the body sizepathological shadows from 1 to 10 mm means that dissemination occurs. These may be patches of different pathogenesis and morphological structure. They are inflammatory and non-inflammatory, fibrosing. In general, it can be a collection of tissues and cells. In the area of inflammatory foci, a process of perifocal nature occurs. In addition, such areas tend to merge. At the same time, they begin to resemble the infiltrative-pneumonic process. With the defeat of the lungs bilateral pathology is noted. Here it is necessary to mention some differences in the diagnosis. Previously, such processes were commonly called diffuse lung diseases. However, a total defeat may not always be observed. In this regard, the name "disseminated" in this case is more appropriate. Changes may not be diffuse.

Symptoms
Dissemination is x-raydefinition, which includes about a hundred different diseases. They can occur with all sorts of symptoms. Dissemination in the lungs is usually accompanied by an inflammatory process of the pleura. The symptoms are twofold. In inflammatory diseases, a syndrome of intoxication and hypoxia occurs. Against the background of disseminated lung cancer and carcinomatosis, respiratory failure progresses with the further development of pathology. Pulmonary dissemination difficult to diagnose. That is why there is a high probability of error. For a more accurate diagnosis requires a complete examination of patients.
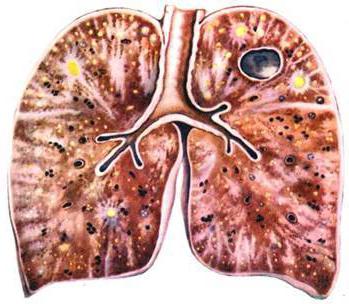
Classification of pathologies
Diseases for which dissemination occurs are:
- Alveolitis (toxic fibrosing, exogenous allergic alveolitis, Hammen-Rich syndrome, microlithiasis, proteinosis);
- granulomatosis (pneumoconiosis, sarcoidosis, disseminated tuberculosis, pneumomycosis, histiocytosis);
- inflammation associated with tumor formations (carcinomatosis, bronchoalveolar, metastatic cancer);
- rare diseases (Goodpasture syndrome, idiopathic hemosiderosis, leiomyomatosis);
- interstitial fibrosis, which are formed when other organs and systems are damaged (collagenosis, radiation damage, cardiogenic sclerosis, as well as sclerosis with liver disease).

Symptoms
Along with the general, there are individualsigns indicating the development of disseminated processes. Knowledge and ability to recognize them make diagnosis much easier. With pulmonary fibrosis, a moderate narrowing of the lung fields occurs. Their transparency is also reduced. Changes in the tuberculous form are located in the upper lung. But diffuse pneumosclerosis is more pronounced in the lower part. Cancer metastases are located singly in the middle lung, and there is a large number of nodes in carcinomatosis. In tuberculosis, the lesions have various sizes, their localization is subpleural. In the case of pneumoconiosis, the pathological process progresses in the lower lymph nodes, then granulomas appear, then the tissues are sclerosed. The remaining processes of dissemination are much worse diagnosed, therefore a complex of laboratory examinations is necessary.